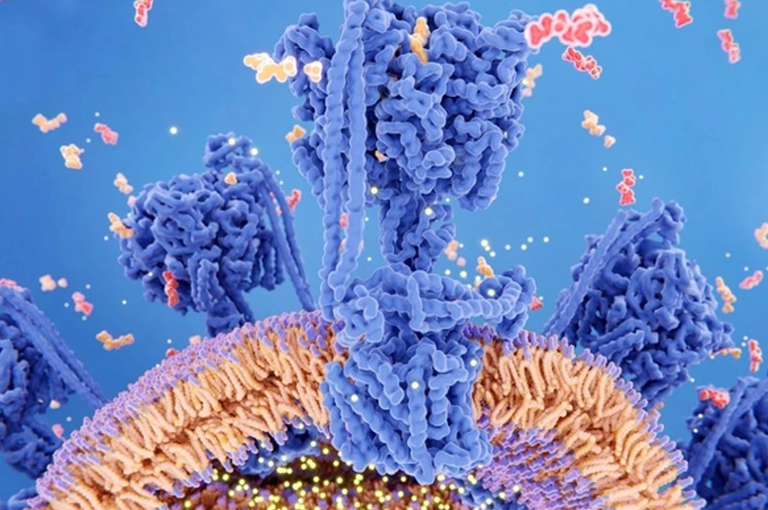
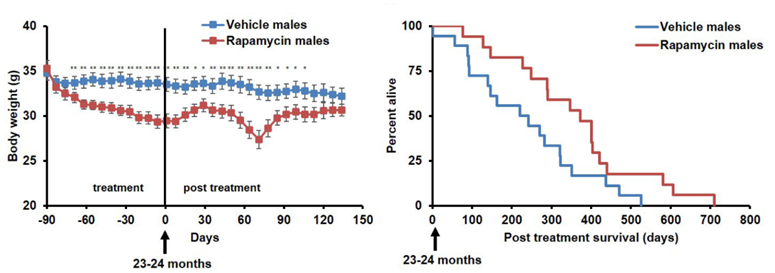
1. Bitto, A., Ito, T. K., Pineda, V. V., LeTexier, N. J., Huang, H. Z., Sutlief, E., Tung, H., Vizzini, N., Chen, B., Smith, K., Meza, D., Yajima, M., Beyer, R. P., Kerr, K. F., Davis, D. J., Gillespie, C. H., Snyder, J. M., Treuting, P. M., & Kaeberlein, M. (2016). Transient rapamycin treatment can increase lifespan and healthspan in middle-aged mice. eLife, 5, e16351. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16351
2. Selvarani, R., Mohammed, S., & Richardson, A. (2021). Effect of rapamycin on aging and age-related diseases-past and future. GeroScience, 43(3), 1135–1158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00274-1
3. Zhang, Z., Xu, H. N., Li, S., Jr, A. D., Chellappa, K., Davis, J. G., Guan, Y., Frederick, D. W., Chu, W., Zhao, H., Li, L. Z., & Baur, J. A. (2020). Rapamycin maintains NAD+/NADH redox homeostasis in muscle cells. Aging, 12(18), 17786–17799. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103954
4. 5053 - PicoLab® Rodent Diet 20 (labdiet.com)


 举报
举报

 京公网安备 11010502053836号
京公网安备 11010502053836号